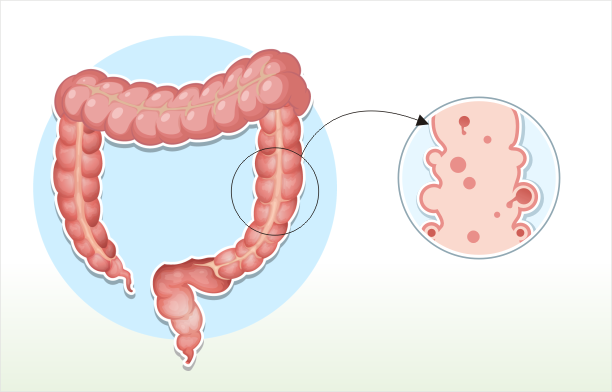
diverticulosis
Diverticular disease is a problem in your intestine. Diverticula are small pouches that bulge outward in the large intestine. Individuals with diverticula are diagnosed with diverticulosis. It is estimated that about 10% of Americans older than age 40 have this condition. If you have diverticulosis, you may not have symptoms, but might notice mild cramps, bloating, and constipation.
If the pockets in the intestines become inflamed or infected, the condition is called diverticulitis. Both diverticulosis and diverticulitis are forms of diverticular disease, but diverticulitis is serious and requires medical treatment.
FAQ
What causes diverticulosis?
The exact cause is not entirely clear, but it is associated with factors such as aging, a low-fiber diet, and a sedentary lifestyle. A diet low in fiber can lead to increased pressure in the colon, contributing to the formation of diverticula.
What are the symptoms of diverticulosis?
Most people with diverticulosis do not experience symptoms. However, some individuals may develop symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Complications such as diverticulitis (inflammation of the diverticula) can cause more severe symptoms.
How is diverticulosis diagnosed?
Diverticulosis is often diagnosed through imaging studies, such as a colonoscopy or a CT scan of the abdomen. These tests can visualize the presence of diverticula and assess the overall condition of the colon.
Can diverticulosis be prevented?
Adopting a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity can help prevent diverticulosis. These lifestyle measures promote healthy bowel movements and reduce the risk of diverticula formation.
What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is the inflammation or infection of the diverticula. It can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and changes in bowel habits. In severe cases, diverticulitis can lead to complications like abscess formation or perforation of the colon.
How is diverticulitis treated?
Treatment for diverticulitis may involve antibiotics to manage infection, a clear liquid diet to allow the colon to rest, and in some cases, hospitalization for more severe cases or complications. Surgery may be necessary for recurrent or complicated cases.
Can diverticulosis lead to complications?
While most people with diverticulosis do not experience complications, diverticulitis (inflammation or infection of the diverticula) and other complications such as abscess formation, perforation, or fistula formation can occur and require medical attention.
Are there risk factors for developing diverticulosis?
Risk factors include aging, a low-fiber diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, and smoking. Genetics may also play a role. Individuals with these risk factors should consider adopting a lifestyle that promotes digestive health.
Can diverticulosis be managed through diet?
Yes, a high-fiber diet is often recommended for managing diverticulosis. Fiber helps soften stool and prevent constipation, reducing pressure in the colon. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary recommendations based on individual health conditions.