Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person and may alternate between diarrhea and constipation. IBS causes discomfort and often is upsetting, but it does not harm the intestines or lead to diseases such as cancer.
FAQ
What causes IBS?
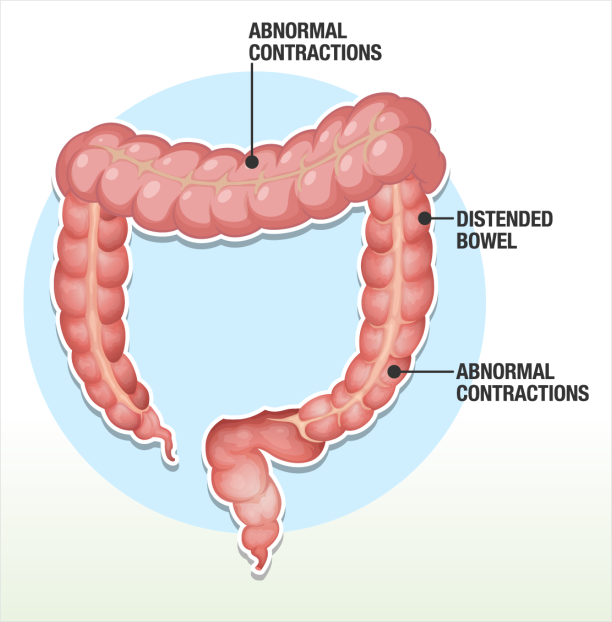
The exact cause of IBS is unclear, but factors such as abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines, changes in gut bacteria, and heightened sensitivity to certain stimuli can contribute to its development.
What are the symptoms of IBS?
Symptoms include abdominal pain or discomfort, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits. Some people experience predominantly diarrhea (IBS-D), constipation (IBS-C), or a mix of both (IBS-M).
How is IBS diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on symptoms, medical history, and the exclusion of other gastrointestinal disorders. In some cases, tests such as blood tests, stool tests, or colonoscopy may be performed to rule out other conditions.
Can stress trigger or worsen IBS symptoms?
Yes, stress and emotional factors can influence IBS symptoms. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and lifestyle changes may help in symptom management.
Are there specific dietary triggers for IBS?
Dietary triggers vary among individuals. Common triggers include certain foods like dairy, high-fat items, spicy foods, caffeine, and artificial sweeteners. Keeping a food diary can help identify specific triggers.
How is IBS treated?
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and stress management are often recommended. Medications may be prescribed to alleviate specific symptoms like diarrhea or constipation.
Can IBS be cured?
IBS is a chronic condition, and there is no cure. However, symptoms can often be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and, in some cases, medications.
Are there different types of IBS?
Yes, IBS is often categorized into subtypes based on the predominant bowel habits. These include IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D), IBS with constipation (IBS-C), and mixed-type (IBS-M).
When should I see a doctor about IBS symptoms?
If you experience persistent or severe gastrointestinal symptoms, it’s advisable to see a doctor. This is especially important if symptoms are accompanied by weight loss, blood in the stool, or if you are over the age of 50 and experiencing new-onset symptoms. A healthcare professional can help with diagnosis and management.